Computer Programs – Concepts
Let's start with the concepts of computer programming: computer programs, algorithms, programming languages, code compilation and execution.
Video: Computer Programs, Compilers, Interpreters
Watch a video lesson about the concepts of programming, programs, compilers and interpreters here: https://youtu.be/U16C61p6m1k.
What It Means "To Program"?
To program means to give commands to the computer, for example "to play a sound", "to print something on the screen" or "to multiply two numbers". When the commands are one after another, they are called a computer program. The text of computer programs is called a program code (or a source code, or even shorter – code).
Example of command for the computer:
Console.WriteLine("Welcome to coding");
Run the above code example: https://repl.it/@nakov/welcome-to-coding-csharp.
When executed, the above command prints the following text:
Welcome to coding
Computer Programs
Computer programs represent a sequence of commands that are written in certain programming language, like C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, C++, PHP, C, Ruby, Swift, Go or another.
Example of computer program in C#:
using System;
class SquareArea
{
public static void Main()
{
var size = 5;
Console.WriteLine("Size = " + size);
Console.WriteLine("Area = " + size * size);
}
}
Run the above code example: https://repl.it/@nakov/square-area-csharp.
The above program defines a class SquareArea, holding a method Main(), which holds a sequence of 3 commands:
- Declaring and assigning a variable:
var size = 5; - Calculating and printing an expression:
Console.WriteLine("Size = " + size); - Calculating and printing an expression:
Console.WriteLine("Area = " + size * size);
The result (output) from the above program is as follows:
Size = 5
Area = 25
We shall explain in detail how to write programs in C#, why we need to define a class and why we need to define a method Main() a bit later. Now, assume that the C# language requires all the above code in order to execute a sequence of command.
In order to write commands, we should know the syntax and the semantics of the language which we are working with, in our case – C#. Therefore, we are going to get familiar with the syntax and the semantics of the language C#, and with programming generally, in the current book, by learning step by step code writing from the simpler to the more complex programming constructions.
Algorithms
Computer programs usually execute some algorithm. Algorithms are a sequence of steps, necessary for the completion of a certain task and for gaining some expected result, something like a "recipe".
For example, if we fry eggs, we follow some recipe (an algorithm): we warm up the oil in a pan, break the eggs inside it, wait for them to fry and move them away from the stove.
Similarly, in programming the computer programs execute algorithms: a sequence of commands, necessary for the completion of a certain task. For example, to arrange a sequence of numbers in an ascending order, an algorithm is needed, e.g. find the smallest number and print it, then find the smallest number among the rest of the numbers and print it, and this is repeated until there are no more numbers left.
For convenience when creating programs, for writing programming code, for execution of programs and other operations related to programming, we need a development environment, for example Visual Studio.
Programming Languages, Compilers, Interpreters and Development Environments
Let's review some concepts from computer programming: programming languages, compilers, interpreters and development environments (IDEs).
Programming Languages
A programming language is an artificial language (syntax for expression), meant for giving commands that we want the computer to read, process and execute. Using programming languages, we write sequences of commands (programs), which define what the computer should do. Examples of programming languages are C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, C, C++, PHP, Swift, Go and many others. These languages differ in their philosophy, syntax, purpose, programming constructions and execution environment. The execution of computer programs can be done with a compiler or with an interpreter.
Compilers
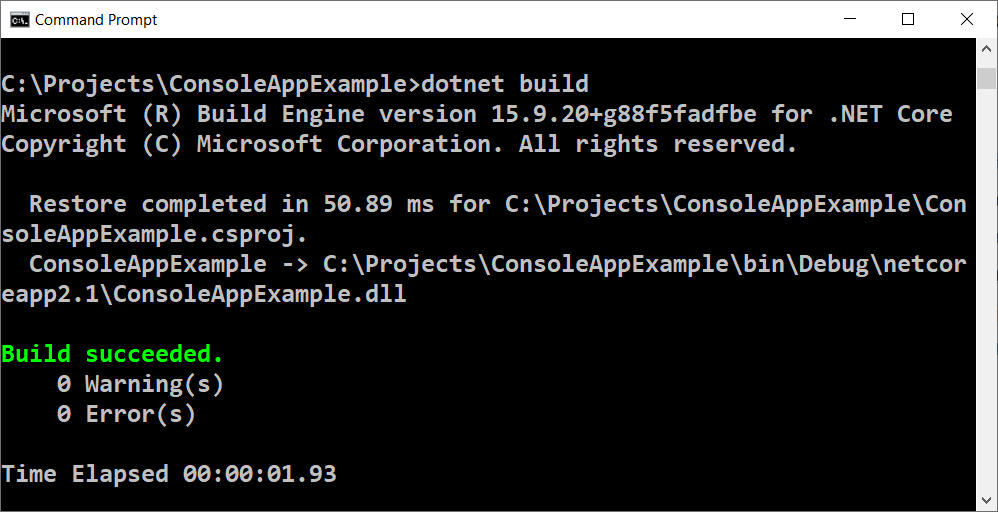
The compiler translates the code from programming language to machine code, as for each of the constructions (commands) in the code it chooses a proper, previously prepared fragment of machine code and in the meantime it checks the text of the program for errors. Together, the compiled fragments comprise the program into a machine code, as the microprocessor of the computer expects it. After the program has been compiled, it can be executed directly from the microprocessor in cooperation with the operating system. With compiler-based programming languages the compilation of the program is done obligatory before its execution, and syntax errors (wrong commands) are found during compile time. Languages like C++, C#, Java, Swift and Go work with a compiler. This an example how the compiler execution may look (the console-based dotnet compiler):
Interpreters
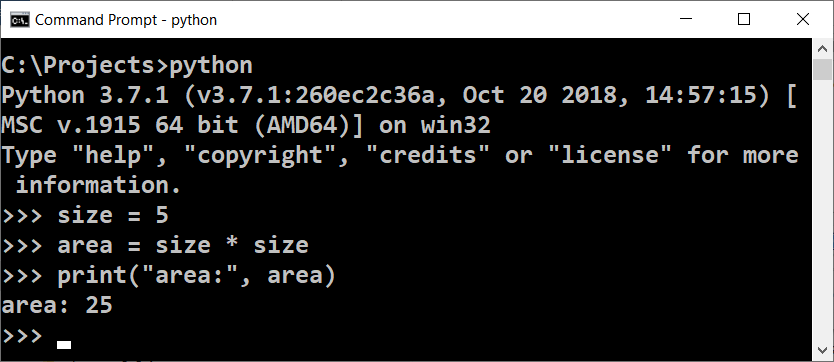
Some programming languages do not use a compiler and are being interpreted directly by a specialized software called an "interpreter". The interpreter is "a program for executing programs", written in some programming language. It executes the commands in the program one after another, as it understands not only a single command and sequences of commands, but also other language constructions (evaluations, iterations, functions, etc.). Languages like Python, PHP and JavaScript work with an interpreter and are being executed without being compiled. Due to the absence of previous compilation, in interpreted languages the errors are being found during the execution time, after the program starts running, not previously. This is an example how an interpreter may look (the python interpreter in the console):
Development Environments (IDE)
An environment for development (Integrated Development Environment – IDE) is a combination of traditional tools for development of software applications. In the development environment we write code, compile and execute the programs. Development environments integrate in them a text editor for writing code, a programming language, a compiler or an interpreter and a runtime environment for executing programs, a debugger for tracking the program and seeking out errors, tools for user interface design and other tools and add-ons.
Environments for development are convenient, because they integrate everything necessary for the development of the program, without the need to exit the environment. If we don't use an environment for development, we will have to write the code in a text editor, to compile it with a command on the console, to run it with another command on the console and to write more additional commands when needed, which is very time consuming. That is why most of the programmers use an IDE in their everyday work.
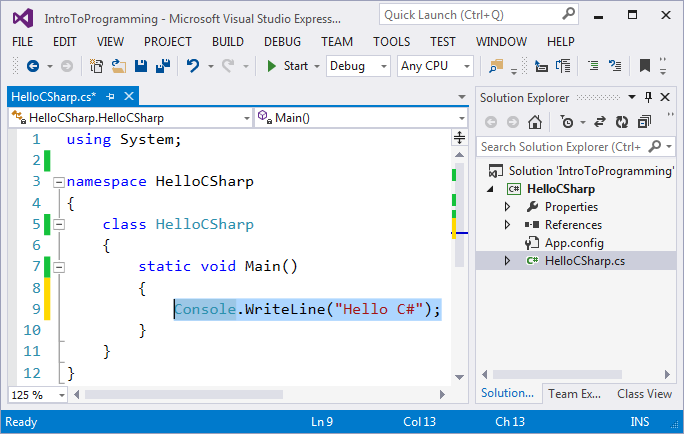
For programming with the C# language the most commonly used IDE is Visual Studio, which is developed and distributed freely by Microsoft and can be downloaded from: https://www.visualstudio.com/downloads/. Alternatives of Visual Studio are:
- Rider – https://www.jetbrains.com/rider
- MonoDevelop / Xamarin Studio – https://www.monodevelop.com
- Visual Studio Code - https://code.visualstudio.com
- Eclipse aCute – https://projects.eclipse.org/projects/tools.acute
In the current book, we are going to use the development environment Visual Studio. This an example how a development IDE may look (the Visual Studio IDE for C#):