Problem: Vegetable Market
A gardener is selling his harvest on the vegetables market. He is selling vegetables for N coins per kilogram and fruits for M coins per kilogram. Write a program that calculates the earnings of the harvest in Euro (EUR). Assume the EUR / coin rate is fixed: 1 Euro == 1.94 coins.
Input Data
Four numbers are read from the console, one per line:
- First line: vegetable price per kilogram – a floating-point number.
- Second line: fruit price per kilogram – a floating-point number.
- Third line: total kilograms of vegetables – an integer.
- Fourth line: total kilograms of fruits – an integer.
Constraints: all numbers will be within the range from 0.00 to 1000.00.
Output Data
Print on the console one floating-point number: the earnings of all fruits and vegetables in Euro.
Sample Input and Output
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| 0.194 19.4 10 10 |
101 |
Clarification for the first example:
- Vegetables cost: 0.194 coins * 10 kg = 1.94 coins.
- Fruits cost: 19.4 coins * 10 kg = 194 coins.
- Total: 195.94 coins = 101 euro (== 101 * 1.94).
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| 1.5 2.5 10 10 |
20.6185567010309 |
Hints and Guidelines
First, we will give a few ideas and particular hints for solving the problem, followed by the essential part of the code.
Idea for Solution
Let's first go through the problem requirements. In this case, we have to calculate the total income from the harvest. It equals the sum of the earnings from the fruits and vegetables which we can calculate by multiplying the price per kilogram by the quantity. The input is given in coins and the output should be in EUR. It is assumed that 1 Euro equals 1.94 coins, therefore, in order to get the wanted output value, we have to divide the sum by 1.94.
Choosing Data Types
After we have a clear idea of how to solve the task, we can continue with choosing appropriate data types. Let's go through the input: we have two integers for total kilograms of vegetables and fruits, therefore, the variables we declare to store their values will be of int type. The prices of the fruits and vegetables are said to be floating-point numbers and therefore, the variables will be of double type.
We can also declare two variables to store the income from the fruits and vegetables separately. As we are multiplying a variable of int type (total kilograms) with one of double type (price), the result should also be of double type. Let's clarify that: generally, operators work with arguments of the same type. Therefore, in order to multiply values of different data types, we have to convert them into the same type. When there are types of different scopes in one expression, the one with the highest scope is the one the other types are converted to, in this case, double. As there isn't danger of data loss, the conversion is implicit and is automatically done by the compiler.
The output should also be a floating-point number and therefore, the result will be stored in a variable of double type.
Solution
It is time to get to the solution. We can divide it into three smaller tasks:
- Reading input from the console.
- Doing the calculations.
- Printing the output on the console.
In order to read the input, we declare variables, which we have to name carefully, so that they can give us a hint about the values they store. With Console.ReadLine(…), we read values from the console and with the functions int.Parse(…) and double.Parse(…), we convert the particular string value into int and double.

We do the necessary calculations:
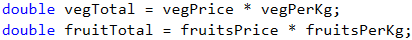
The task does not specify special output format. Therefore, we just have to calculate the requested value and print it on the console. As in mathematics and so in programming, division has a priority over addition. However, in this task, first we have to calculate the sum of the two input values and then divide by 1.94. In order to give priority to addition, we can use brackets. With Console.WriteLine(…) we print the output on the console.
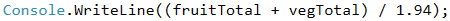
Testing in the Judge System
Test your solution here: https://judge.softuni.org/Contests/Practice/Index/505#1.