Do-While Loop
The next type of loops we will get familiar with are the do-while loops. By structure, this type of loop resembles the while loop, but there is a significant difference between them. It is that the do-while loop will execute its body at least once. Why is this happening? In the do-while loop construction, the condition is always checked after the body, which ensures that the first loop iteration will execute the code and the check for the end of the loop will be applied to each subsequent iteration of the do-while.
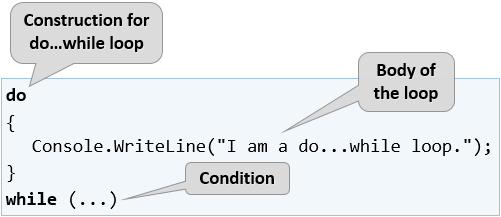
Now let’s proceed to the usual set of sample practical problems follows. Their solutions will help us better understand the do-while loops.
Video: Do-While Loop
Watch a video lesson about the do-while loop and how to use it: https://youtu.be/hEJ9-lNyahU.
Example: Calculating Factorial
For natural n number, calculate n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * … * n. For example, if n = 5, the result will be: 5! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 = 120.
Here is how we can specifically calculate factorial:
- We create the variable
nto which we assign an integer value taken from the console input. - We create another variable – a
factwhich initial value is 1. We will use it for the calculation and storage of the factorial. - For a loop condition, we will use
n > 1, because each time we perform the calculations in the body of the loop, we will decrease the value ofnby 1. - In the body of the loop:
- We assign a new value to
factthat is the result of multiplying the currentfactvalue to the current value ofn. - We decrease the value of
nby -1.
- We assign a new value to
- Outside the body of the loop, we print the final factorial value.
This is a sample code, implementing the above described steps:

Testing in the Judge System
Test your solution here: https://judge.softuni.org/Contests/Practice/Index/514#7.