More Complex Conditions – Examples
Sometimes the conditions may be very complex, so they can require a long bool expression or a sequence of conditions. Let's take a look at a few examples.
Example: Point on a Rectangle Border
Write a program that checks whether a point {x, y} is placed onto any of the sides of a rectangle {x1, y1} – {x2, y2}. The input data is read from the console and consists of 6 lines: the decimal numbers x1, y1, x2, y2, x and y (as it is guaranteed that x1 < x2 and y1 < y2). Print "Border" (if the point lies on any of the sides) or "Inside / Outside" (in the opposite case).
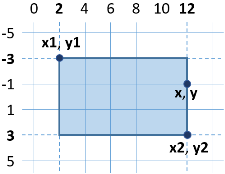
Sample Input and Output
| Input | Output | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 -3 12 3 12 -1 |
Border | 2 -3 12 3 8 -1 |
Inside / Outside |
Solution
The point lies on any of the sides of the rectangle if:
- x coincides with x1 or x2 and at the same time y is between y1 and y2 or
- y coincides with y1 or y2 and at the same time x is between x1 and x2.

The previous evaluation might be simplified in the following way:

The second way with the additional Boolean (bool) variables is longer, but much more understandable than the first one, isn't it? We recommend when you write Boolean conditions to make them easy to read and understand, instead of making them short. Use additional variables with meaningful names, if needed. The names of the bool variables have to hint what the value that is kept inside them represents.
What remains is to finish writing the code to print “Inside / Outside”, if the point is not onto any of the sides of the rectangle.
Testing in the Judge System
After you finish writing the solution, you can test it here: https://judge.softuni.org/Contests/Practice/Index/508#5.
Example: Fruit Shop
A fruit shop during week days sells in the following prices:
| Fruit | Price |
|---|---|
| banana apple orange grapefruit kiwi pineapple grapes |
2.50 1.20 0.85 1.45 2.70 5.50 3.85 |
During the weekend days the prices are higher:
| Fruit | Price |
|---|---|
| banana apple orange grapefruit kiwi pineapple grapes |
2.70 1.25 0.90 1.60 3.00 5.60 4.20 |
Write a program that reads from the console a fruit (banana / apple / …), a day of the week (Monday / Tuesday / …) and a quantity (a decimal number) and calculates the price according to the prices from the tables above. The result has to be printed rounded up to 2 digits after the decimal point. Print “error” if it is an invalid day of the week or an invalid name of a fruit.
Sample Input and Output
| Input | Output | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| orange Sunday 3 |
2.70 | kiwi Monday 2.5 |
6.75 |
| Input | Output | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| grapes Saturday 0.5 |
2.10 | tomato Monday 0.5 |
error |
Video: Fruit Store
Watch the video to learn how to solve the "Fruit Store" problem: https://youtu.be/6vZZzil9xBU.
Solution

Testing in the Judge System
Test your solution here: https://judge.softuni.org/Contests/Practice/Index/508#6.
Example: Trade Fees
A company is giving the following commissions to its traders according to the city, in which they are working and the volume of sales s:
| City | 0 <= s <= 500 | 500 < s <= 1000 | 1000 < s <= 10000 | s > 10000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sofia Varna Plovdiv |
5% 4.5% 5.5% |
7% 7.5% 8% |
8% 10% 12% |
12% 13% 14.5% |
Write a program that reads the name of a city (string) and the volume of sales (decimal number) and calculates the rate of the commission fee. The result has to be shown rounded up to 2 digits after the decimal point. When there is an invalid city or volume of sales (a negative number), print "error".
Sample Input and Output
| Input | Output | Input | Output | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sofia 1500 |
120.00 | Plovdiv 499.99 |
27.50 | Paris -50 |
error |
Video: Trade Fees
Watch the video about the "Trade Fees" problem and its solution: https://youtu.be/QqKBLJ4JzJ0.
Solution
When reading the input, we could convert the city into small letters (with the function .ToLower()). Initially we set the commission fee to -1. It will be changed if the city and the price range are found in the table of commissions.
To calculate the commission according to the city and volume of sales, we need a few nested if statements, as in the sample code below:

Testing in the Judge System
Test your solution here: https://judge.softuni.org/Contests/Practice/Index/508#7.
It is a good practice to use blocks that are enclosed with curly braces { } after if and else. Also, it is recommended during writing to move aside the code after if and else with a single tabulation inward, in order to make the code more easily readable. |